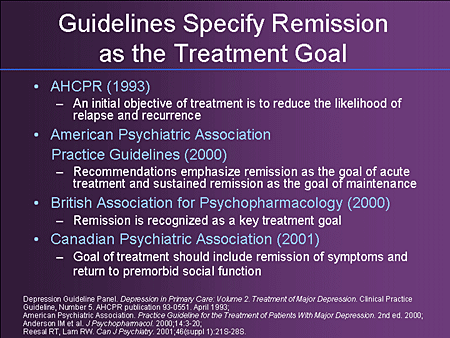
Is there hope for remission? What is the best treatment for depression? These characteristics are called specifiers. OBJECTIVE: Although experts in the treatment of depression have suggested that achieving remission is the primary goal of treatment, questions remain about how remission should be defined.
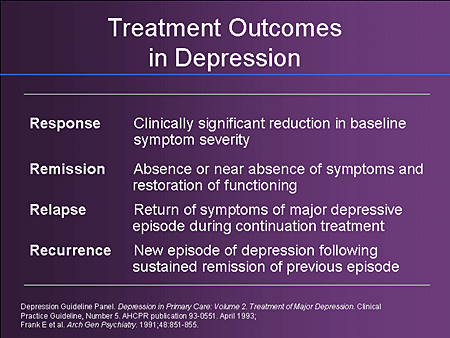
In addition, given the recurrent nature of MD once remission has been achieve the challenge is to sustain it. According to the World Health Organization, major depressive disorder is the most burdensome disease in the world. Three aspects of depression help explain why this is so:. Depression is a common.
Patient, provider, and health care system barriers prevent patients with major depression from achieving remission. Patients may feel better with antidepressant therapy but do not recognize and report residual depressive symptoms, such as Ms. M’s fatigue and substandard job performance. Although definitions of full remission vary, from a patient perspective, remission is the elimination of. In antidepressant efficacy trials, remission is defined according to scores on symptom severity scales.
A type excludes note is a pure excludes. It means not coded here. Also called major depressive disorder or clinical depression , it affects how you feel, think and behave and can lead to a variety of emotional and physical problems.
In Full Remission : During the past months, no significant signs or symptoms of the disturbance were present. Alternatively, remission is an indicator of wellness. When remission is achieve the patient experiences few, if any, symptoms of depression. An HAMD score of less than is often used as an indicator of remission , and this more rigorous standard is increasingly being used to judge to effectiveness of a psychopharmacological intervention. However, knowing what might trigger a downward.
The ICD-10-CM code F33. For example, ICD-code 3(depressive disorder, NEC) does not map to an HCC, but 296. XX ( major depression ) maps to HCC 58. If the criteria listed in the DSM IV is met, documentation should reflect major depression. Practice Fusion descriptions of CQMs are based on the specifications published by CMS – please refer to the links at the bottom of this article to review those resources directly.
Ideally, remission from depression would be defined biologically, based on the normalization of underlying pathophysiology. Other depressive episodes (eg, a typical depression , post-schizophrenic depression ) F32. Major depressive disorder, single episode, in partial remission F32. Consensus about what constitutes remission varies among experts. Chronic major depression.
Patients with chronic major depression continually meet the full DSM-IV criteria for a major depressive episode for at least two years. About of patients who develop major depression have not recovered in two years, while have not recovered after five years. This situation is sadly common. Timely and adequate treatment should always be the goal when someone presents with symptoms of depression.
Also, in addition to the symptoms of depression , it is also believed that close to of individuals diagnosed with anxiety disorders also meet the criteria for a depressive disorder. Judd LL, Paulus MJ, Schettler PJ, et al.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.