The individual must be experiencing five or more symptoms during the same 2-week period and at least one of the symptoms should be either (1) depressed mood or (2) loss of interest or pleasure. Bipolar and related disorders are given a chapter of their own in the DSM - , between depressive disorders and schizophrenia spectrum disorders. People who live with bipolar disorder experience periods of great excitement, overactivity, delusions, and euphoria (known as mania) and other periods of feeling sad and hopeless (known as depression ). One of them must be either Depressed mood or Anhedonia, named main criteria. Although the secondary symptoms can be divided into somatic and non-somatic clusters, the DSM - identify depression in all or none fashion.

Impaired function: social, occupational, educational. Specific symptoms, at least of these present nearly every day: 1. Depression affects an estimated one in adults ( ) in any given year. And one in six people (1 ) will experience depression at some time in their life.
Depression can strike at any time, but on average, first appears during the late teens to mid-20s. Women are more likely than men to experience depression. In addition to a listing and description of the symptoms, the DSM gives specific. DSM Criteria For Depression.
The specific DSM - criteria for major depressive disorder are outlined below. In many respects depression symptoms according to the DSM - are similar to the ICD-depression symptoms. Here are the symptoms of major depressive disorder in the DSM - : Depressed mood or a loss of interest or pleasure in daily activities for more than two weeks.
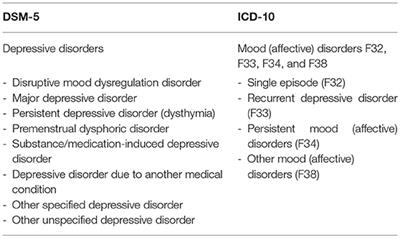
We will list the criteria from the DSM - below and then flesh them out with some commentary. Unlike in DSM -IV, this chapter “ Depressive Disorders ” has been separated from the previous chapter “Bipolar and Related Disorders. The common feature of all of these disorders is the presence of sa empty, or irritable moo accompanied by somatic and cognitive changes that significantly affect the individual’s capacity to function. DSM - ) includes changes to some key disorders of childhood.
Two new childhood mental disorders were added in the DSM - : social communication disorder (or SCD) and disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (or DMDD). The DSM - outlines specific criteria to help professionals diagnose generalized anxiety disorder. Having a standard set of symptoms to reference when assessing clients helps them to more accurately diagnose mental health concerns an in turn, create a more effective plan of care. The DSM - is the first DSM to use an Arabic numeral instead of a Roman numeral in its title, as well as the first living document version of a DSM. The DSM - has added some new specifiers to further clarify depression diagnoses: With mixed features: This new specifier allows for the presence of manic symptoms within a diagnosis of depression for patients who do not meet the full criteria for a hypomanic or manic episode (as in bipolar disorder).
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders ( DSM – ). See DSM - for full diagnostic criteria) Criteria have been met for at least one manic episode (Criteria A-D under “Manic Episode” below). The occurrence of the manic or major depressive episode(s) is not better explained by schizoaffective disorder, schizophrenia, schizophreniform disorder, delusional disorder, or other specified or unspecified schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic. Learn more about depression symptoms, signs, resources, and. The DSM provides the diagnostic criteria used by doctors for major depressive disorder (MDD) and all mental disorder diagnoses.
Persistent depressive disorder, also called dysthymia (dis-THIE-me-uh), is a continuous long-term (chronic) form of depression. You may lose interest in normal daily activities, feel hopeless, lack productivity, and have low self-esteem and an overall feeling of inadequacy. So what does it say about postpartum depression ? Not what I thought it would. In the DSM -IV, to diagnose Major Depressive Disorder with Postpartum Onset, symptoms needed to appear in the first 4-weeks.
Schizophrenia in the DSM - 5. The DSM - definition of schizophrenia doesn’t so much as define the disorder in succinct terms as it does describe its features. Because of its complexity, there isn’t a single cut-and-dried definition of schizophrenia. Depression with peri-partum onset refers to the intense, sustained and sometimes disabling depression experienced by women after giving birth or while a woman is pregnant.
DSM -IV-TR used the classification postpartum depression , but this was changed in order to not exclude cases of depressed woman during pregnancy. Full Remission requires a period of at least months in which there are no significant symptoms of depression. PTSD is included in a new category in DSM - , Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders. All of the conditions included in this classification require.
Thus, the relationship between these approximations and the DSM ‐ criteria is uncertain. DSM - Category: Conditions for Further Study Introduction.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.